The LAMP stack is an open-source software package popular for web development. It consists of four (4) key components: Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB, and PHP.
Apache is a software that provides a platform for hosting web-based programs, such as websites and applications on various operating systems, including the Linux-based CentOS system.
MySQL/MariaDB provides the database functionality, which is necessary for storing and managing dynamic content in web applications. Additionally, It is integrated with the PHP package.
PHP, a server-side scripting language, interacts with databases and easily generates dynamic content for web browsers.
This procedural guide will configure the LAMP stack on your CentOS 9 system.
How to Install the LAMP Stack on CentOS 9?
To configure the LAMP stack on your CentOS 9 machine, you are required to install the following packages:
- How to Setup Apache Service on CentOS 9 System?
- How to Configure MariaDB Package on the CentOS 9 System?
- How to Setup PHP Module on CentOS 9 System?
Step 1: Update CentOS 9 System Files
The updated system files improve the performance of the CentOS 9 system. Thus, keep your CentOS using the following code:
sudo yum update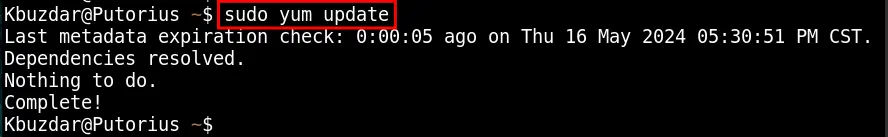
This system is already updated, as mentioned above. Ensure, you have a similar message on your terminal.
How to Setup Apache Service on CentOS 9 System?
These steps will contribute to installing the Apache package on your CentOS 9 machine.
Step 1: Install Apache on CentOS 9
For installing and configure the Apache server on your CentOS 9, copy the below command to your terminal:
sudo yum install httpd -y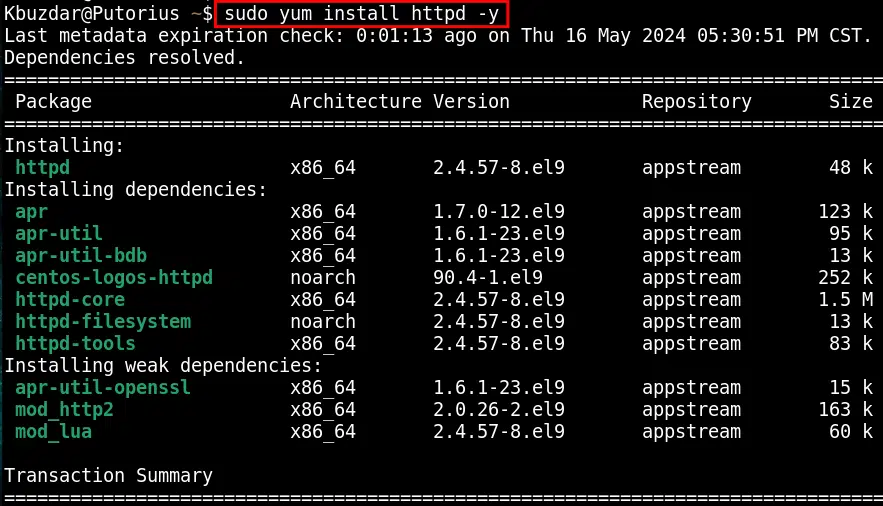
When the setup process is completed, a message of completion will be returned to your screen.
Step 2: Enable Apache
You can enable the Apache server through the command:
sudo systemctl enable httpd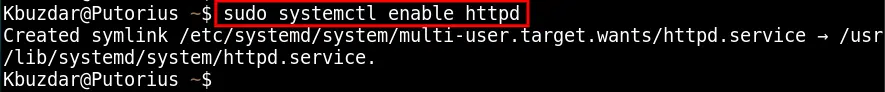
This command successfully enabled the Apache services via the terminal.
Step 3: Start Apache
To start the Apache services, simply copy the following command to your CentOS terminal:
sudo systemctl start httpd
If there is nothing returned in your output, indicating that Apache is started on your system.
Step 4: Check Apache Service Status
Using the given below command, you can check the Apache service’s current status:
sudo systemctl status httpd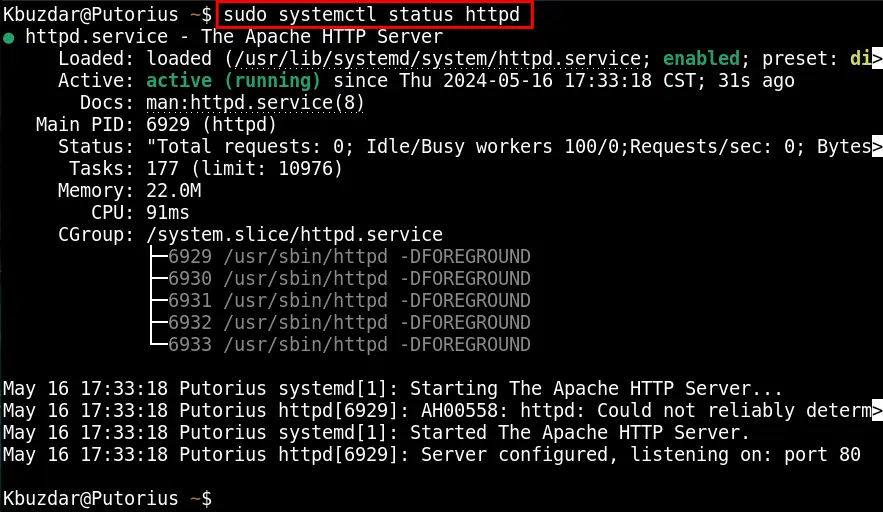
How to Configure MariaDB Package on the CentOS 9 System?
The below sequential process will install the MariaDB package on your CentOS 9 system.
Step 1: Install MariaDB
Utilize the command mentioned below to configure the MariaDB (MySQL) on your CentOS 9 system:
sudo yum install mariadb-server mariadb -y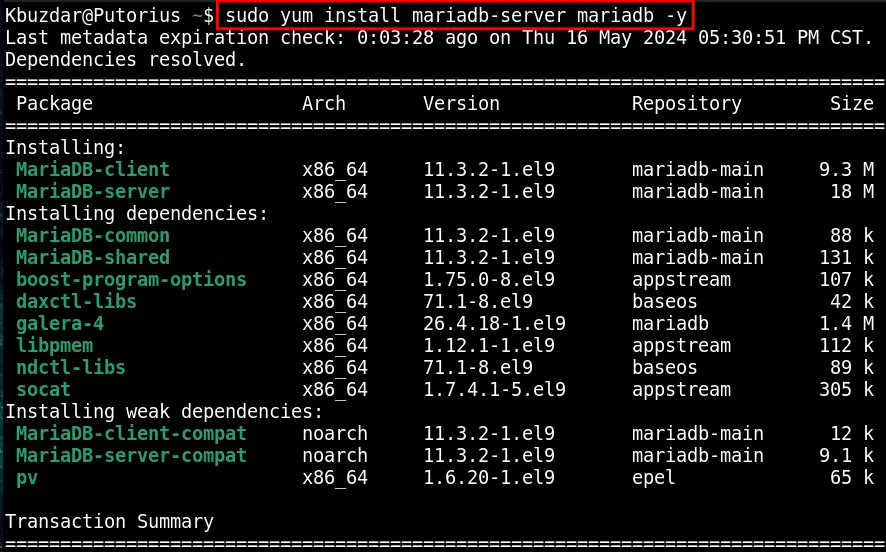
The command returned that the MariaDB has been configured on your CentOS system.
Step 2: Enable MariaDB
After installing the MariaDB package on your machine, you are required to enable the MariaDB services via the command given below:
sudo systemctl enable mariadb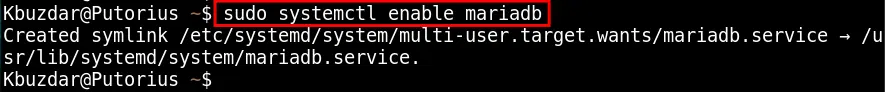
The MariaDB service is now enabled on your system.
Step 3: Start MariaDB
You are also required to start the MariaDB services using the command:
sudo systemctl start mariadb
Blank output means that you have successfully executed the start command.
Step 4: Check MariaDB Service Status
Finally, confirm the service status of MariaDB through the command:
sudo systemctl status mariadb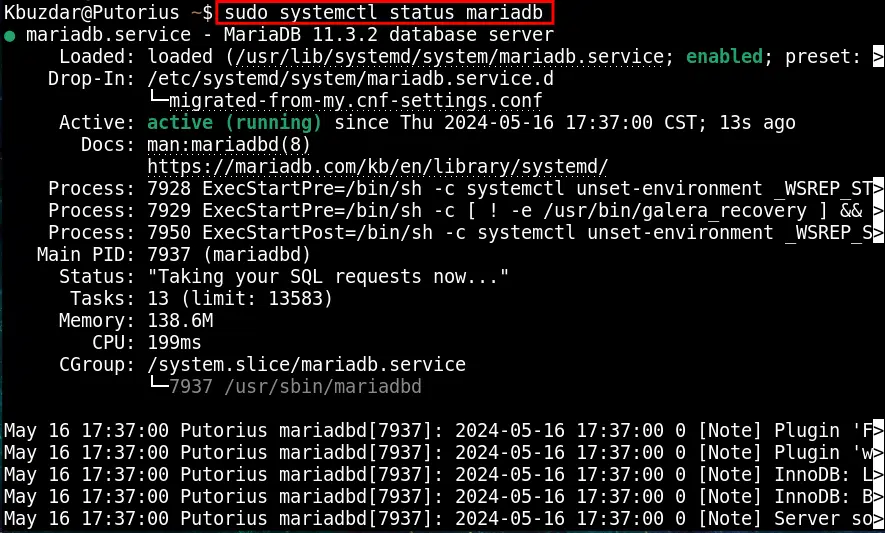
Step 5: Check Version MariaDB/MySQL
To confirm the version or release number of the MariaDB, use the “-V” option:
mariadb -V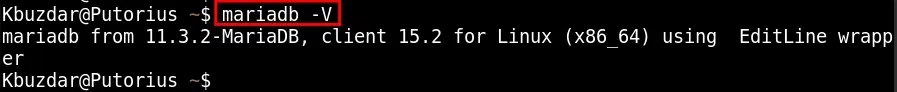
As mentioned above, the MariaDB 11.3.2 has been configured on your system.
How to Setup PHP Modules on CentOS 9 System?
To install PHP modules on your CentOS 9 system, follow these necessary steps.
Step 1: Display Available PHP Modules
Before installing the PHP modules, first, display the list of available modules via the command:
sudo yum module list php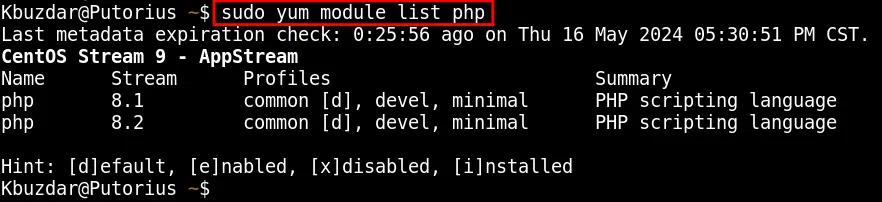
The above list shows that you can either install the php8.1 or php8.2 on your CentOS 9 system.
Step 2: Enable the PHP Module
After choosing the version number from the available PHP module list, you need to enable that version, for example:
sudo yum module enable php:8.2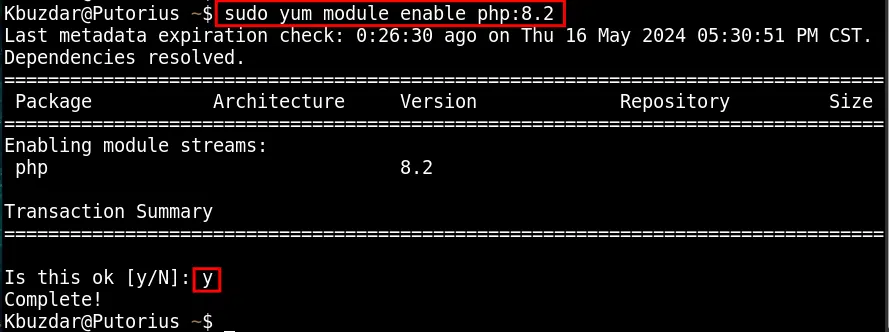
Step 3: Install PHP
Now, you can install the PHP modules by copying the command to your CentOS 9 terminal:
sudo yum install php php-cli php-gd php-curl php-zip php-mbstring php-mysqlnd -y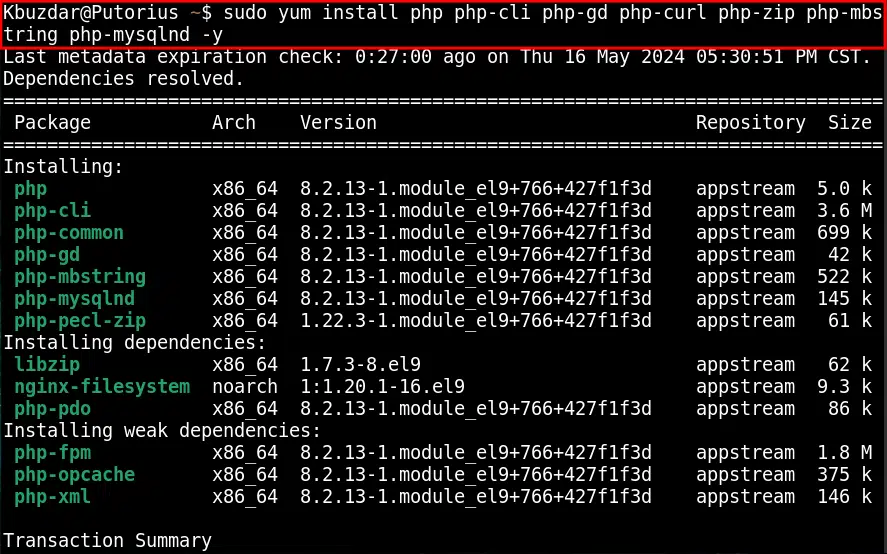
You can monitor the various modules which have been installed for the PHP 8.2 package.
Step 4: Confirm PHP Installation
To verify the installed version of PHP, utilize the command as mentioned below:
php -v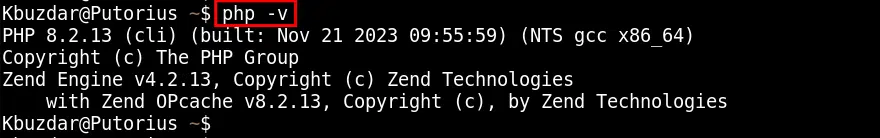
Here is the latest version such as 8.2.13 of the PHP package on your CentOS 9 system.
Step 5: Restart Apache
Finally, you are required to restart Apache for PHP changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart httpdThis command will reboot the Apache server and as a result all the necessary changes will take effect.
Step 6: Create “info.php” Test File
To test PHP services, first create a file name “info.php” using the command:
sudo nano /var/www/html/info.phpSimply, copy the following brief code to your “info.php” file:
<?php
phpinfo();
?>This script will display the detailed information about PHP. Simply, save your file by using Ctrl + S.
Step 7: Access “info.php” Page
Once you have done all the above steps, open your web browser and copy the below-mentioned link to your address bar:
localhost/info.php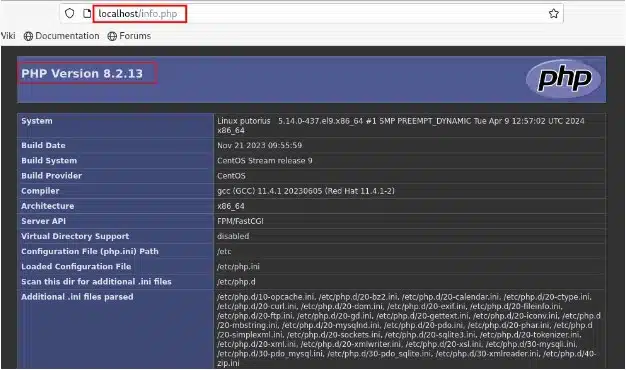
If you see a message, such as “PHP Version 8.2.13” on your screen, it indicates that you have successfully installed the LAMP stack on your CentOS 9 system.
Conclusion
LAMP stack can be configured on CentOS 9 through a simple procedure. For example, first, set up the Apache server with the command “sudo yum install httpd -y”. Secondly, configure the MariaDB/MySQL package “sudo yum install mariadb-server mariadb -y”. Lastly, set up the PHP modules on your system. Hence, you have configured the LAMP stack on your CentOS 9 machine.
Links and Resources:
Join Our Newsletter
Categories
- Bash Scripting (17)
- Basic Commands (51)
- Featured (7)
- Just for Fun (5)
- Linux Quick Tips (98)
- Linux Tutorials (65)
- Miscellaneous (15)
- Network Tools (6)
- Reviews (2)
- Security (32)
- Smart Home (1)

